Portrait Weekly Framing: Perplexity's $34.5B Chrome Bid Signals New Era of Tech Antitrust Risk
Welcome to this week's edition of the Portrait Weekly Framing. Today, we'll be examining the implications of Perplexity's unsolicited $34.5 billion offer for Google's Chrome browser and what this unprecedented bid reveals about regulatory risk across Big Tech.
Alphabet Inc. (GOOGL.UR)
The artificial intelligence startup Perplexity's offer to acquire Google's Chrome browser for $34.5 billion represents a watershed moment in technology sector regulation. This bid, which is nearly double Perplexity's own $18 billion valuation, arrives as U.S. District Judge Amit Mehta prepares to rule this month on remedies for Google's illegal search monopoly. The offer marks the first serious external attempt to acquire a core asset from a Big Tech giant under antitrust pressure, signaling that the regulatory environment has shifted from theoretical risk to actionable market opportunity.
Chrome's strategic importance extends far beyond its 3.5 billion users and 60% global browser market share. The browser serves as the primary gateway to Google's $265 billion annual advertising revenue, functioning as what industry experts describe as a critical strategic asset when considering its role in maintaining Google's digital position. Perplexity's bid, backed by several large venture capital funds according to the Wall Street Journal, explicitly positions itself as "designed to satisfy an antitrust remedy in highest public interest by placing Chrome with a capable, independent operator."
The timing and magnitude of this offer suggest that investors are beginning to price in a potential restructuring of Big Tech's competitive landscape. Barclays analysts have warned that a forced Chrome sale could trigger a 15-25% decline in Google stock, while the precedent could affect other major technology companies. With Judge Mehta expected to rule by the end of August 2025, and similar antitrust actions pending against other tech giants, understanding the regulatory risk exposure across major technology platforms has become important for portfolio positioning. To quantify this risk and identify potential implications, I used Portrait's Research tool to analyze the regulatory landscape:
Analyze regulatory risk exposure across GOOGL, META, AMZN, AAPL, and MSFT, focusing on potential divestiture scenarios and their impact on revenue streams over the next 12 months. Include current antitrust cases, regulatory investigations, and specific business segments most vulnerable to forced separation. Quantify the revenue at risk for each company and assess the likelihood of regulatory action based on recent precedents and political dynamics.
The analysis revealed that all five tech giants face material regulatory proceedings, though the nature and timing of these risks vary considerably. Google confronts the most immediate challenge with its search monopoly ruling already decided and remedies imminent, while Meta faces both an FTC divestiture lawsuit targeting Instagram and WhatsApp and near-term European revenue pressures. Amazon's integrated marketplace model and Apple's App Store commission structure both face scrutiny, with Apple also facing potential criminal contempt proceedings. Microsoft, while less exposed to breakup risk, must navigate questions about its cloud bundling practices and its $13 billion OpenAI partnership. The research identified that over $500 billion in annual revenue across these companies could be affected by regulatory action, with several key decisions expected within the next 12 months.
Big Tech Regulatory Risk Analysis: A Multi-Front Assault on Core Business Models
The largest U.S. technology companies—Alphabet, Meta, Amazon, Apple, and Microsoft—are facing an unprecedented and coordinated wave of regulatory scrutiny across multiple jurisdictions. This assault, led by agencies in the United States and the European Union, has moved beyond theoretical risk to encompass active litigation, significant legal defeats, and explicit threats of structural change. The core business models that have driven decades of growth and profitability are now under direct attack, with regulators targeting everything from search and advertising dominance to app store commissions and cloud computing practices. For investors, this creates a complex and material overhang, with the potential for forced divestitures, significant fines, and mandated changes to business practices that could directly impact revenue streams over the next 12 months and beyond.
This analysis examines the specific regulatory risk exposure for each company, focusing on the most significant legal proceedings, the business segments most vulnerable to forced separation or change, and the quantifiable revenue at risk.
Alphabet (GOOGL): Existential Threats to Search and Ad Tech
Alphabet is confronting the most advanced and multi-pronged regulatory assault of its peers, with recent court rulings confirming antitrust violations in its core Search and Google Play businesses. The primary risk is no longer whether regulators will act, but what form the court-ordered remedies will take, with the potential for structural separation of its key business units.
Key Proceedings and Vulnerable Segments
Alphabet is fighting landmark cases on three critical fronts:
DOJ Search Lawsuit: In a significant blow, a U.S. District Court ruled in August 2024 that Google illegally monopolized the search market. The case has now entered a remedies phase, with the DOJ seeking "structural remedies" that could fundamentally alter how Google operates its most profitable business (GOOGL 10-Q Q1 2025).
DOJ Ad Tech Lawsuit: A January 2023 lawsuit explicitly seeks the divestiture of Google's ad-tech stack. A mixed ruling in April 2025 found its publisher ad server violated antitrust laws, keeping the prospect of a forced breakup on the table pending appeal (GOOGL 8-K 04/17/25 Other Events, GOOGL 10-Q Q1 2025).
Google Play Litigation: Following a December 2023 jury verdict finding its Play store practices anticompetitive in the Epic Games case, the Ninth Circuit Court of Appeals affirmed this verdict on July 31, 2025 (News - 2025Q3 - GOOGL.UR). This makes it highly likely that Google will be forced to implement a court-ordered injunction mandating significant, revenue-dilutive changes to its app store model (GOOGL 10-Q Q3 2024).
European Commission (EC) DMA Probes: The EC has opened non-compliance investigations into Google's Search and Play store practices under the Digital Markets Act (DMA), with preliminary findings of non-compliance issued in March 2025 (GOOGL 10-Q Q1 2025).
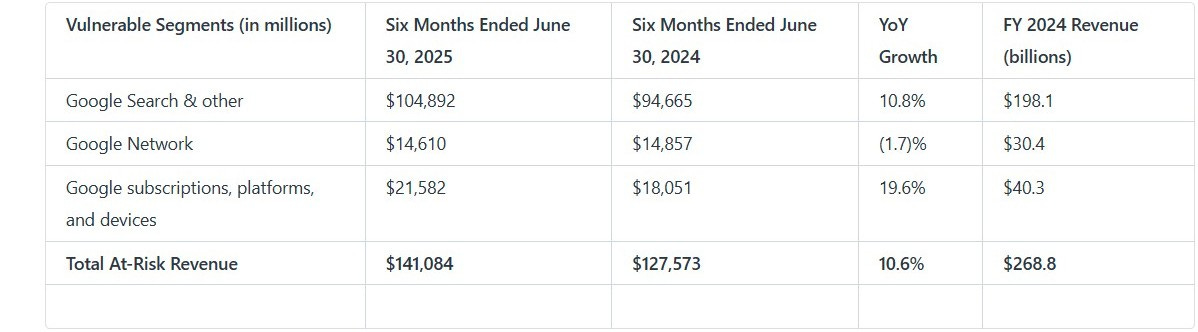
Revenue at Risk
The legal proceedings target the vast majority of Alphabet's revenue. The Google Search, Network (Ad Tech), and Subscriptions (Google Play) segments collectively represent the core of the company's financial engine. The scale of this exposure is substantial, with these segments continuing to grow even as legal risks mount.
Likelihood and Impact: The likelihood of significant, forced changes to Alphabet's business is high. The adverse liability ruling in the DOJ Search case and the failure of the Epic Games appeal are critical setbacks. The key catalyst in the next 12 months will be the remedies decision in the Search case, expected in late 2025. A forced divestiture of the Ad Tech business remains a distinct possibility, while court-ordered changes to the Google Play store are now highly probable. The tangible costs are already appearing, with a recent shareholder settlement requiring a $500 million investment in compliance infrastructure (GOOGL.UR 8-K 07/08/25 Other Events).
Meta Platforms (META): Divestiture Risk and an Imminent European Revenue Hit
Meta faces a dual threat: an existential legal challenge in the U.S. seeking to break up the company, and an immediate, quantifiable revenue risk in Europe stemming from new platform regulations. Management has been unusually explicit in warning of a near-term negative impact from European rules.
Key Proceedings and Vulnerable Segments
FTC Divestiture Lawsuit: The FTC's lawsuit, which concluded its trial phase in May 2025, seeks the forced divestiture of Instagram and WhatsApp, alleging they were acquired to illegally maintain a social networking monopoly (META 10-Q Q1 2025). A final court decision is anticipated in late 2025 or early 2026 (META.UR 10-Q Q2 2025). A loss would fundamentally dismantle the company's integrated "Family of Apps" (FoA) strategy.
EC DMA/DSA Regulations: Meta's "subscription for no ads" model, introduced to comply with EU privacy rules, was rejected by the EC in April 2025, resulting in a €200 million fine (META.UR 10-Q Q2 2025). Meta is appealing but has warned it must modify its model, which could have a "significant negative impact on our European revenue, as early as later this quarter" (META.UR 8-K 07/30/25 Earnings Release).
Revenue at Risk
The entire FoA segment, which accounts for over 99% of company revenue, is targeted by the FTC. More immediately, the European portion of that revenue is vulnerable to regulatory changes. Europe accounted for nearly a quarter of Meta's core FoA revenue in the first half of 2025.
Likelihood and Impact: The impact from European regulations is both highly likely and imminent. Management's repeated and specific warnings suggest a material revenue headwind beginning in Q3 2025 is a base-case scenario. The FTC divestiture case represents a lower-probability but catastrophic-impact risk; a ruling against Meta would be transformative. The combination of these two fronts places Meta in a uniquely precarious position over the next 12 months.
Amazon (AMZN): Marketplace and Cloud Models Under Fire
Amazon's regulatory challenges are aimed at the heart of its e-commerce flywheel and its highly profitable cloud business. A landmark U.S. antitrust case threatens to dismantle the integrated practices that link its marketplace, logistics, and advertising services, while AWS faces separate scrutiny.
Key Proceedings and Vulnerable Segments
FTC & State AG Marketplace Lawsuit: Filed in September 2023, this suit alleges Amazon illegally maintains monopoly power by coercing sellers into using its Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) service and using anticompetitive pricing policies to stifle competition (AMZN 10-Q Q3 2024). The court's denial of Amazon's motion to dismiss in September 2024 ensures the case will proceed (AMZN 10-K FY 2024). The complaint explicitly seeks "structural relief," putting divestiture on the table.
AWS Scrutiny: The company discloses ongoing investigations into "certain aspects of AWS’s offering of cloud services," indicating that its most profitable division is not immune from regulatory pressure (AMZN 10-K FY 2024).
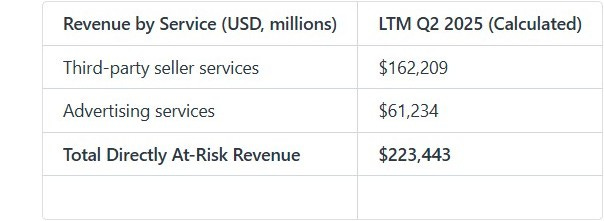
Revenue at Risk
The business lines directly targeted by the FTC—Third-party seller services and Advertising services—are large, high-growth revenue streams. For the last twelve months (LTM) ending Q2 2025, these services generated a combined $223.4 billion. Any remedy impacting these high-margin services would disproportionately affect profitability.
Likelihood and Impact: The likelihood of some form of remedy is medium-to-high, given the case is proceeding. While a full structural separation of the marketplace from Amazon's retail operations is a tail risk, court-ordered changes to FBA tying or pricing policies are more probable. Such changes would threaten the high-margin service revenues that are critical to the profitability of the North America segment, which posted $13.4 billion in operating income in H1 2025 (AMZN.UR 10-Q Q2 2025).
Apple (AAPL): "Walled Garden" Under Siege
Apple is defending its highly profitable, tightly integrated ecosystem against a coordinated assault from the DOJ and the EC. The primary target is the Services segment, specifically the App Store's commission-based model, which regulators allege is protected by anticompetitive control over the iPhone.
Key Proceedings and Vulnerable Segments
DOJ Monopolization Lawsuit: A March 2024 lawsuit alleges Apple monopolizes the smartphone market by suppressing competing technologies like super apps and cloud streaming services (AAPL.UR 10-Q Q3 2025). Apple's motion to dismiss was rejected in June 2025, signaling a lengthy legal battle ahead (News - 2025Q3 - AAPL.UR).
EC DMA Enforcement: The EC is aggressively targeting App Store rules, fining Apple €500 million in April 2025 for its "anti-steering" policies and opening a new probe into its DMA compliance plan (AAPL.UR 10-Q Q3 2025). Non-compliance could lead to fines of up to 10% of global revenue.
Epic Games Injunction: In a major escalation, a U.S. court found Apple in violation of a 2021 injunction related to its anti-steering rules on April 30, 2025. The court issued a stricter order and, critically, referred Apple to the U.S. Attorney for potential criminal contempt proceedings (AAPL.UR 10-Q Q3 2025).
Revenue at Risk
The Services segment is the clear target. This segment is a crucial driver of profitability, with a gross margin of 75.6% in the most recent quarter—more than double that of Products (AAPL.UR 10-Q Q3 2025). Any forced reduction in App Store commissions or allowance of alternative payment systems without a fee would directly hit Apple's bottom line.
Likelihood and Impact: The likelihood of forced, material changes to the App Store business model is high. The combination of the DOJ lawsuit, aggressive EC enforcement, and the stunning criminal contempt referral in the Epic case creates immense pressure. While management has downplayed the financial impact to date, it is difficult to see how the current 15-30% commission structure survives intact in the long term. A forced change would significantly impair the growth and profitability of Apple's most important segment.
Microsoft (MSFT): Scrutiny on Cloud Bundling and AI Dominance
Microsoft's regulatory risk differs from its peers, focusing less on past acquisitions and more on current business practices. Regulators are examining whether Microsoft is illegally bundling its dominant software products with its Azure cloud platform and whether its deep partnership with OpenAI constitutes a de facto merger that stifles competition in the nascent AI market.
Key Proceedings and Vulnerable Segments
Cloud and Software Bundling: Regulators in the U.S. and Europe are scrutinizing the integration of Microsoft 365 with Azure, concerned that this practice unfairly disadvantages competing cloud providers (MSFT.UR 10-K FY 2025, Microsoft Corporation, Q3 2025 Earnings Call, Apr 30, 2025 (Presentation)).
OpenAI Partnership Review: Competition authorities are investigating Microsoft's $13 billion investment in OpenAI as a potential merger that could consolidate power in the AI space (MSFT 10-Q Q2 2025). This risk is compounded by reports of internal friction, with OpenAI executives reportedly considering an anticompetitive complaint against Microsoft (News - 2025Q2 - MSFT.UR).
Revenue at Risk
The scrutiny targets Microsoft's two largest and most profitable segments: Productivity and Business Processes and Intelligent Cloud. Together, these segments accounted for 81% of total revenue and 89% of total operating income in Q3 FY25, making any remedy highly material. The "Microsoft Cloud" revenue metric, which aggregates the key at-risk services, reached $42.4 billion in the last quarter.
Likelihood and Impact: The likelihood of a behavioral remedy, such as forced unbundling or mandated interoperability, is medium-to-high. A structural breakup is highly unlikely. The primary risk is a constraint on future growth and margins rather than a dismantling of the current business. The unique risk posed by the potential unraveling of the OpenAI partnership, independent of regulatory action, could significantly disrupt Microsoft's AI strategy, which is a key pillar of its current investment thesis.
Table Sources:
Alphabet: GOOGL.UR 10-Q Q2 2025, GOOGL 10-K FY 2024
Meta Platforms: META.UR 10-Q Q2 2025
Amazon: Calculated from AMZN.UR 10-Q Q2 2025 and AMZN 10-K FY 2024
Apple: Calculated from AAPL.UR 10-Q Q3 2025
Microsoft: MSFT 10-Q Q3 2025
With this comprehensive understanding of the regulatory landscape, the next challenge becomes tracking how these risks evolve in real-time. The volume of legal proceedings, regulatory filings, and court decisions across multiple jurisdictions makes it difficult for investors to maintain situational awareness through traditional research methods. Each company faces multiple simultaneous proceedings that could materialize at any moment—a court ruling on Google's Chrome divestiture, an FTC decision on Meta's Instagram and WhatsApp ownership, or new European Commission penalties that could reach 10% of global revenue. To address this challenge, I configured a Monitor in Portrait to track regulatory developments across these companies systematically:
Companies: GOOGL, META, AMZN, AAPL, MSFT
Datapoints to Find: Regulatory developments including antitrust rulings, divestiture orders, regulatory fines, changes to business model requirements, new investigations or lawsuits filed, settlement agreements, and management commentary on regulatory impacts. Include both U.S. and international regulatory actions, with particular focus on DOJ, FTC, and European Commission proceedings.
The Monitor revealed a pattern of regulatory actions unfolding across Big Tech, with Google facing immediate pressure through the Chrome divestiture proceedings, while Apple confronts criminal contempt referral and Meta warns of near-term European revenue impacts. The tracking system identified over 40 distinct regulatory proceedings across the five companies in just the past quarter, ranging from the UK Competition and Markets Authority's designation of "strategic market status" for certain platforms to Italy's investigation into Meta's AI integration with WhatsApp. The Monitor also captured management's increasingly specific warnings about financial impacts, with Meta's leadership stating that European regulatory feedback could have "significant negative impact on our European revenue, as early as later this quarter," while Google faces a potential €4.12 billion Android fine alongside the Chrome divestiture proceedings.
Regulatory Developments Monitor
The global regulatory environment for major technology firms is characterized by escalating pressure across multiple fronts, including antitrust, privacy, and the burgeoning field of artificial intelligence. Regulators in the U.S., European Union, and United Kingdom are moving from investigations to enforcement actions, including significant fines, court-mandated business model changes, and the credible threat of structural remedies like divestitures.
Alphabet (Google)
Google faces the most acute and tangible divestiture risk among its peers, with the forced sale of its Chrome browser emerging as a serious potential remedy in U.S. antitrust proceedings. This threat has been amplified by a formal $34.5B acquisition offer from Perplexity and public interest from OpenAI's Sam Altman. Simultaneously, the company is battling adverse court rulings that mandate changes to its core business models, while navigating a complex and diverging set of AI regulations globally.
Antitrust - U.S.:
(-) Divestiture Risk: The potential forced sale of the Chrome browser has become a credible threat, representing a material escalation in the ongoing U.S. antitrust case.
(-) Epic Games Ruling: A U.S. appeals court upheld the verdict in the Epic Games case, forcing Google to revamp its Play Store and in-app billing practices. This represents a final, material legal setback.
(-) New Lawsuits: The company faces a new antitrust lawsuit from adtech firm OpenX, adding to legal pressure on its digital advertising business.
Antitrust - International:
(-) European Union: An Advocate General of the EU Court of Justice recommended dismissing Google's appeal of a €4.12B fine in the Android antitrust case, making it highly likely the penalty will be upheld. The company also faces new EU antitrust complaints from publishers regarding its AI Overviews feature and from digital rights groups over app uninstallation.
(-) United Kingdom: The Competition and Markets Authority (CMA) has formally proposed designating Google with 'strategic market status' (SMS) for its mobile platform, general search, and search advertising. This is a significant step toward imposing new conduct requirements, with a final decision expected by October 2024.
(-) Australia: A federal court found Google's app store practices to be anticompetitive in the Epic Games case, increasing legal risk in the region.
(-) Turkey: A new competition probe has been launched into Google's AI-powered PMAX advertising product.
(+) Mexico: In a rare positive development, Mexico's antitrust authority closed a multi-year investigation into Google's ad business, clearing the company.
AI & Privacy Regulation:
(-) Privacy Fine: A California jury ordered Google to pay a $314M penalty for misusing Android user data.
(-) Germany: Google has refused a request from the Berlin Data Protection Commissioner to remove the DeepSeek AI app, escalating the risk of enforcement action under the EU's Digital Services Act (DSA).
(+) EU AI Pact: Google has signaled a cooperative stance by agreeing to sign the EU's AI code of practice.
Autonomous Vehicles (Waymo):
(+) NHTSA Probe Closed: The U.S. National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) closed its investigation into Waymo's automated driving system, removing a key regulatory overhang.
Apple
Apple is engaged in a multi-front battle against regulators globally, with its App Store business model at the center of numerous antitrust challenges. While the company appears poised to de-escalate a major conflict with the European Commission, it faces intensifying scrutiny in the U.K. and a landmark monopoly lawsuit from the U.S. Department of Justice. On a positive note, Apple successfully negotiated a crucial exemption from U.S. tariffs, mitigating a significant supply chain risk.
Antitrust - U.S.:
(-) DOJ Lawsuit: A U.S. judge denied Apple's motion to dismiss the DOJ's landmark lawsuit accusing it of monopolizing the smartphone market, allowing the case to proceed.
(-) New Lawsuits: The company faces new antitrust lawsuits from Proton over App Store fees and a threat of legal action from Elon Musk's xAI over app store rankings.
(-) iCloud Lawsuit: A judge ruled Apple must face a consumer lawsuit accusing it of monopolizing the digital storage market with iCloud.
(+) Lawsuit Dismissed: A U.S. court dismissed an antitrust class action lawsuit related to merchant payment fees, a positive legal outcome.
Antitrust - International:
(+) European Union: The European Commission is reportedly likely to accept Apple's revised App Store rules and fees, allowing the company to avoid significant daily fines under the Digital Markets Act (DMA). However, Apple is separately appealing a €500M EU fine.
(-) United Kingdom: The CMA is formally consulting on designating Apple's mobile platform with 'strategic market status' (SMS), a move that would subject it to stricter rules and potential remedies.
(-) Other Jurisdictions: Apple faces an expanded price-fixing investigation in Spain, an adverse ruling in the Netherlands regarding dating app payments, and an anticompetitive finding in Australia's Epic Games case.
Regulatory-Driven Business & Product Changes:
(+/-) U.S. Tariffs: Apple secured a formal exemption from proposed 100% U.S. semiconductor tariffs after committing to a $100B U.S. investment, though uncertainty remains regarding potential reciprocal tariffs from India and Vietnam.
(-) Apple Watch: A U.S. Customs ruling forced Apple to redesign the Blood Oxygen feature for certain Apple Watch models in the U.S.
(+) Data Privacy: The UK dropped its mandate for Apple to provide a backdoor to encrypted data, removing a significant regulatory threat to its privacy stance.
Meta Platforms
Meta is on a collision course with European regulators, with management issuing a stark warning that EU actions could have a "significant negative impact" on European revenue in the near term. The company's confrontational stance on its 'pay-or-consent' model and the EU's AI code of practice signals a period of heightened risk. In the U.S., Meta resolved a major legacy lawsuit but faces new scrutiny over its AI products and data privacy practices.
European Union Headwinds:
(-) Explicit Revenue Risk: Management has warned that feedback from the European Commission on its advertising model could have a "significant negative impact on our European revenue, as early as later this quarter."
(-) DMA Enforcement: The EC has warned Meta that its proposed changes to its 'pay-or-consent' model are insufficient, making daily fines under the DMA highly likely. Meta is reportedly unwilling to make further changes.
(-) AI Regulation: Meta is publicly refusing to sign the EU's voluntary AI code of practice, a confrontational stance that contrasts with peers and could invite stricter future regulation.
(-) Italian Probe: Italy's competition authority has opened a new investigation into Meta over alleged abuse of dominance related to the integration of AI into WhatsApp.
U.S. Regulation & Litigation:
(+) Major Settlement: Meta reached a settlement to end an $8B investor trial over privacy violations, resolving a significant legal overhang.
(-) New AI Scrutiny: The Texas Attorney General has opened an investigation into Meta's AI chatbots for potentially deceptive trade practices. Separately, U.S. senators are calling for a probe into reports of the chatbots having inappropriate conversations with children.
(-) Privacy Rulings: A federal jury found Meta guilty of violating California privacy laws by recording health information from the Flo app. Another court loss highlighted the applicability of a 1960s-era wiretapping law to modern data privacy cases, creating a new legal risk vector.
Amazon
Amazon's regulatory picture is mixed. The company achieved significant, positive milestones for its futuristic logistics and autonomous vehicle ambitions with favorable U.S. regulatory decisions. However, its core e-commerce and cloud computing businesses are facing gathering antitrust storms, particularly in the U.K., where regulators have found AWS's dominance is harming competition.
Positive Regulatory Milestones:
(+) Autonomous Vehicles (Zoox): Amazon's Zoox subsidiary received the first-ever exemption from U.S. federal vehicle safety standards for purpose-built driverless vehicles, and a related NHTSA probe was closed. This is a material positive development for its autonomous vehicle program.
(+) Drones: A proposed U.S. Department of Transportation rule to ease restrictions on long-range drone operations could directly benefit Amazon's ambitions for autonomous package delivery.
Antitrust & Trade Headwinds:
(-) UK Cloud Scrutiny: The UK's CMA has provisionally found that Amazon Web Services' (AWS) dominant position in cloud computing is harming competition. The regulator is being urged to designate AWS with 'strategic market status' (SMS), which would lead to stricter oversight.
(-) U.S. Lawsuit: A U.S. judge has ordered Amazon to face a lawsuit from independent authors alleging the company has monopolized the audiobook market.
(-) U.S. Tariffs: A new executive order suspending 'de minimis' duty-free treatment for many low-value imports could increase costs and operational complexity for Amazon's cross-border e-commerce business.
To further research Google, Meta, Apple, Amazon, Microsoft, or any other company facing regulatory challenges, head over to Portrait today!